How to scroll in Mobile Tests
Introduction
Our engine for Mobile Tests is using Appium to locate and interact with the elements from native and hybrid mobile applications.
Appium does not provide Scroll or Swipe actions.
But we can achieve the same effect with a Flick action or a Move action.
We just have to flick or move in the opposite direction in which we want to scroll or swipe.
Options
1. Using the Flick action
The Flick action requires 3 parameters:
- Locator Type
- Locator
- Offset to flick by
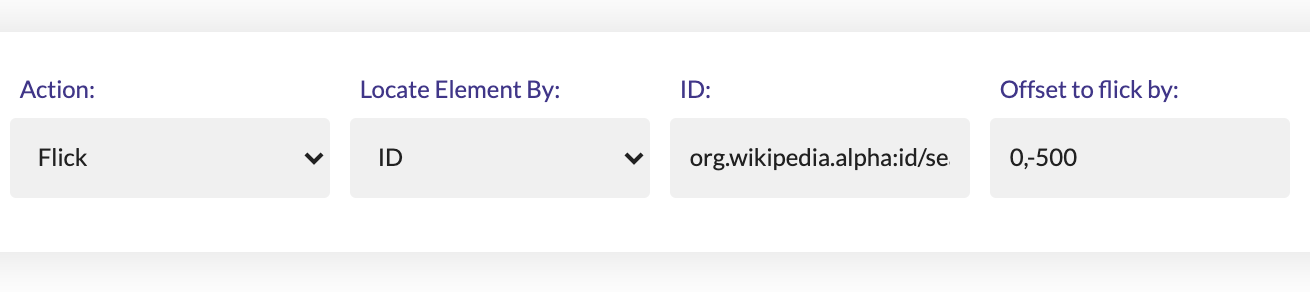
The value for the Offset to flick by is comprised of a value for the X offset and a value for the Y offset, separated by a comma.
The offset is equivalent to the scrolling distance in this case.
As you can see, we need an element in order to flick.
The Flick action does not work with all elements element and there is no attribute to indicate if an element is suitable or not.
If an element is not suitable for the Flick action, it means that performing that action on that element will not result in a scroll on that page.
You will not see any errors in the logs in that case, you will just notice that it has no effect.
This is due to the fact that the element was located and the action was performed, Appium does not throw any errors if the Flick action did not result in a scroll.
The recommended procedure in this case is to try to perform the Flick action with different elements until you find one that works, it's a trial and error process.
For some applications, you might get an error that the
Flickaction is not supported, this is due to the fact that the default versions of Appium used by BrowserStack and Sauce Labs might not support theFlickaction for some applications.In this case, you can try to change the
Appium Versionfrom theSettingssection of that test suite.
2. Using the Move action
The Move action requires 3 parameters:
- Locator Type
- Locator
- Destination
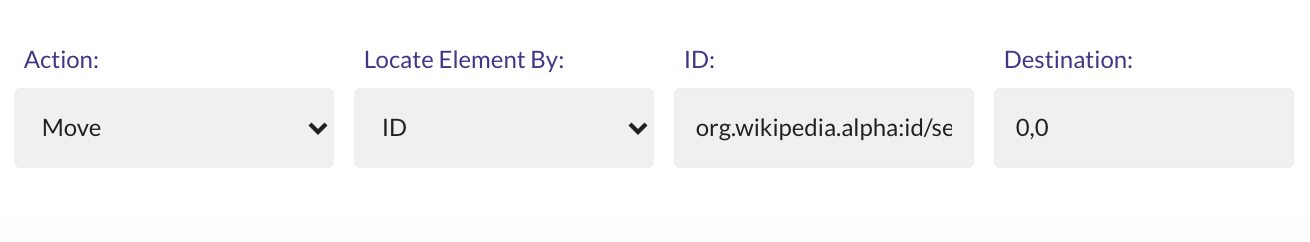
The value for the Destination is comprised of a value for the X coordinate and a value for the Y coordinate, separated by a comma.
As you can see, we need an element in order to move.
The Move action does not work with all elements and there is no attribute to indicate if an element is suitable or not.
If an element is not suitable for the Move action, it means that performing that action on that element will not result in a scroll on that page.
You will not see any errors in the logs in that case, you will just notice that it has no effect.
This is due to the fact that the element was located and the action was performed, Appium does not throw any errors if the Move action did not result in a scroll.
The recommended procedure in this case is to try to perform the Move action with different elements until you find one that works, it's a trial and error process.
Scroll types
1. Scroll down
In order to scroll down, we must flick up or move up.
If we want to use the Flick action, we need to add a negative value for the Y offset:
0, -500
If we want to use the Move action, we need to add a small non-negative value for the Y coordinate:
0, 0
2. Scroll up
In order to scroll up, we must flick down or move down.
If we want to use the Flick action, we need to add a positive value for the Y offset:
0, 500
If we want to use the Move action, we need to add a large non-negative value for the Y coordinate:
0, 500
3. Scroll left
In order to scroll left, we must flick right or move right.
If we want to use the Flick action, we need to add a positive value for the X offset:
500, 0
If we want to use the Move action, we need to add a large non-negative value for the X coordinate:
500, 0
4. Scroll right
In order to scroll right, we must flick left or move left.
If we want to use the Flick action, we need to add a negative value for the X offset:
-500, 0
If we want to use the Move action, we need to add a small non-negative value for the X coordinate:
0, 0
